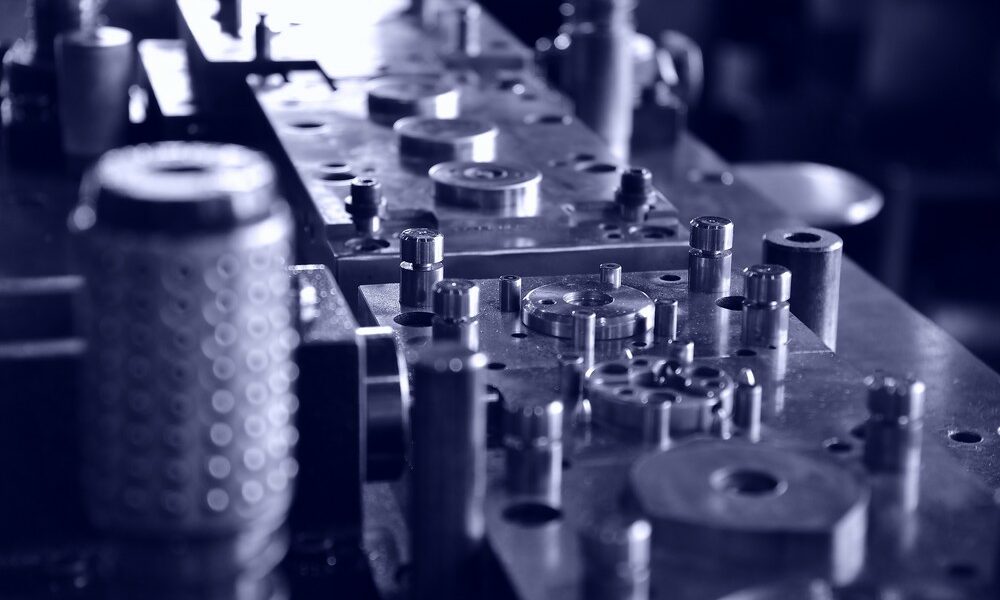
Metal stamping is an important manufacturing process used to create precise, durable parts for various industries. Below, we’ll provide an overview of what metal stamping is, how it’s done, and why it’s an advantageous solution for manufacturers around the world.
Feel free to use this table of contents to navigate to a particular topic of interest:
- What Is Metal Stamping?
- Basic Metal Stamping Processes & Techniques
- Basic Metal Stamping Tools
- Benefits of Metal Stamping vs. Other Manufacturing Processes
What Is Metal Stamping?
Metal stamping is a manufacturing process used to transform metal sheets (often called “blanks”) into different shapes. It uses cold forming techniques, which means that no heat is used to reshape the metal. Instead, the metal is placed between dies and stamping presses that shape and shear it by applying pressure.
A high-speed process, metal stamping is one of the fastest and most cost-effective solutions for manufacturers in need of high-quality components, especially for large-quantity orders.
Metal Stamping Applications
Metal stamping is used for many applications in many different industries. In fact, it’s likely that you use a product with stamped components every day. Whether it be your car, phone, microwave, or any other common household item, metal stamping is a key manufacturing method.
That said, it’d be nearly impossible to list every metal stamping application. But we can list a few of the most common industries:
- Home appliances
- Automotive and transportation
- Building and construction
- Aerospace
- Telecommunications
- Military and defense
- Medical equipment
- Electronics
- Lighting
Basic Metal Stamping Processes & Techniques
Think of metal stamping as the broad manufacturing process here. Within that process, more specialized processes and techniques are employed to achieve a high-quality end result. We’ll walk through a few of those processes and techniques below.
Metal Stamping Processes
There are four main types of metal stamping processes: progressive die stamping, transfer die stamping, four-slide stamping, and fine blanking.
Progressive Die Stamping
Progressive die stamping calls for a series of stamping stations, each of which has a specific function. A metal coil is unrolled into a sheet or strip, then that strip is fed into the die press composed of these various stamping stations. Each station may punch, cut, or bend the metal as it progresses through the press until it reaches the desired shape and size.
Progressive die stamping is great for long-run production. It’s quick, repeatable, and resource-efficient, reducing the amount of wasted scrap metal.
Transfer Die Stamping
Transfer die stamping follows the same general principles as progressive die stamping. However, it separates the metal workpiece from the metal sheet early on, then transfers it to the next stamping station using a mechanical transfer system.
Transfer die stamping comes in handy when you’re working with large components that need multiple presses to achieve the end result.
Four-Slide Stamping
Four-slide stamping (AKA four-way or multi-slide stamping) uses four sliding tools to transform the metal sheet into desired dimensions. Most stamping operations use just one vertical slide, but having four makes it easier to produce more intricate parts with many contortions.
Since so many unique tools can be attached to each of the four slides, four-slide stamping is considered the most versatile stamping process in the industry.
Fine Blanking
Fine blanking uses a mechanical or hydraulic press (or a combination of both) to achieve smooth, precise edges on a metal sheet. These edges can help keep the finished product from cracking, ensuring durability for an extended period of time.
Fine blanking presses require higher operating pressures than those used in other stamping processes. It’s important to keep this in mind when choosing tools and machinery for your production line.
Metal Stamping Techniques
Within each of the more specific stamping processes listed above, various stamping techniques are employed. These can include one or more of the following:
- Punching or perforating removes scrap pieces from the metal sheet as a punch enters the die.
- Blanking removes the desired metal workpiece from the sheet as the punch enters the die.
- Bending forms the sheet metal into desired shapes, like U, V, or L shapes.
- Coining leaves an impression in a metal workpiece’s surface, often in an effort to thin or displace material. It can be applied to just one or both sides of the workpiece. No slug is removed.
- Flanging uses a flange or flare tool to create a joint in the metal sheet, which connects multiple components.
- Embossing deforms a shape within a metal workpiece without intentionally thinning the material.
Basic Metal Stamping Tools
In order to complete metal stamping processes and techniques with accuracy, various tools are needed. These tools can mostly be placed into two categories: metal stamping presses and metal stamping dies.
Metal Stamping Presses
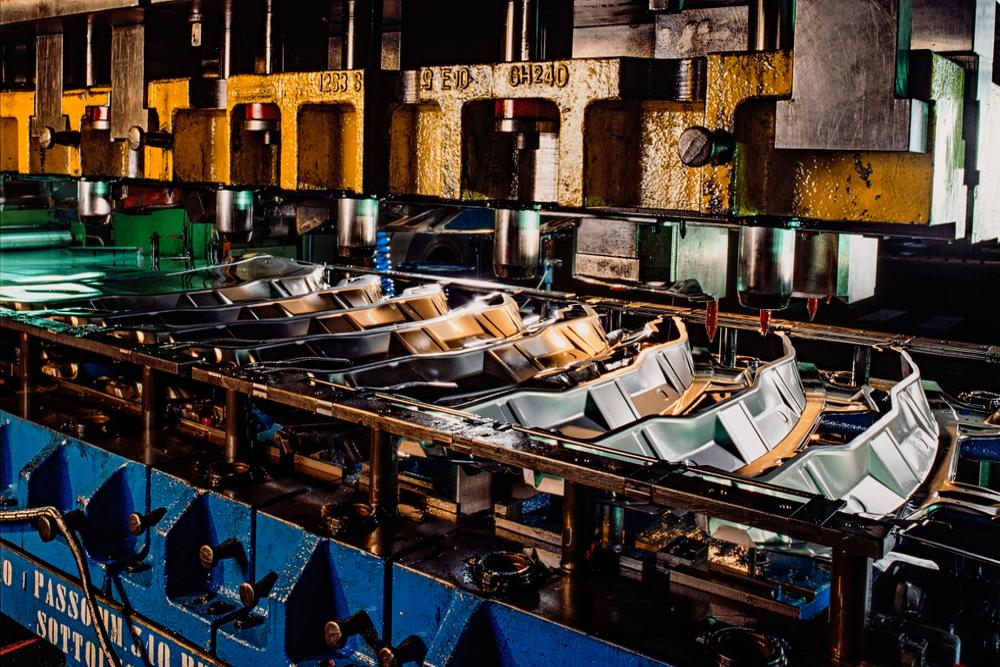
A metal stamping press is the machine used to form, cut, or shape metal into precise shapes by pressing it against a die. Up close, one might look like this. You can see the sheet metal has already been pressed and formed into a specific shape.
There are three common types of metal stamping presses on the market:
- Mechanical presses use motorized mechanical flywheels to transfer and store the energy needed for stamping processes. Their punch sizes range from 5-500mm and their pressing speeds range from 20-1,500 strokes per minute.
- Mechanical servo presses operate similarly to mechanical presses, but employ high-capacity motors instead of flywheels for the transfer and storage of energy. They can be powered by a drive system that allows for programmable stroke, slide position, and speed.
- Hydraulic presses use pressurized hydraulic fluid to achieve the force needed for stamping processes. They offer a more controlled, consistent amount of pressure than mechanical presses do. They also have easily adjustable stroke and speed capabilities, with punch sizes ranging from 10-800mm.
Metal Stamping Dies & Die Components
Metal stamping dies are the tools that actually cut and shape the metal sheet after the press applies pressure. There are two common categories of stamping dies:
- Single-station stamping dies use compound and combinations dies. Compound dies can achieve multiple cuts in a single press. Combination dies can achieve both cutting and non-cutting actions in a single press.
- Multiple station stamping dies use progressive and transfer dies. Both of these dies help achieve multiple punching, cutting, and bending actions in a series from the same die set.
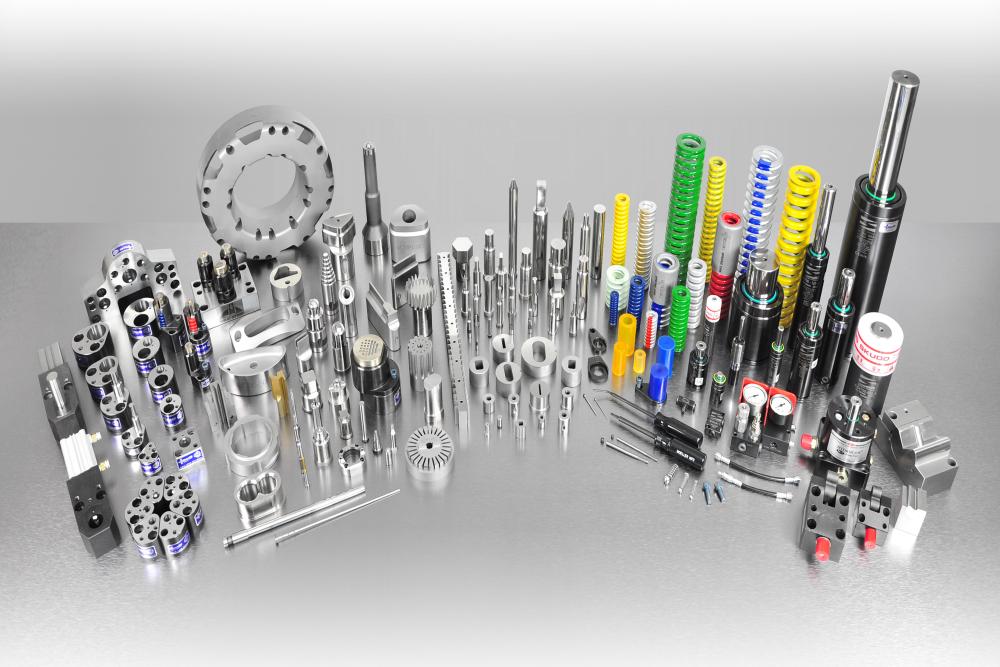
Within all metal stamping dies, there are many smaller die components that help get the job done. Die components can include anything like punches, die buttons, retainers, springs, strippers, accessories, etc. — many of which can be purchased directly from Moeller Precision Tool. And if there’s a certain die component you need that we don’t supply, we can lead you to one of our partners that does.
Benefits of Metal Stamping vs. Other Manufacturing Processes
There’s a reason that metal stamping is one of the most widely used manufacturing processes. Actually, there are a few of them. Here’s an overview of the main benefits metal stamping provides over alternative manufacturing processes:
Unparalleled Precision
The many machines, tools, processes, and techniques used in metal stamping help achieve high-quality, repeatable results. You won’t find a manufacturing method that completes jobs with as much accuracy and precision as these presses and dies do.
Great Automation Opportunities
Looking to increase efficiency throughout the production process? Metal stamping machines are fairly easy to automate. Computer-controlled programming can make all the difference in the accuracy, quality, and turnaround time of your products.
Fast Turnaround Times
Metal stamping is ideal for both short- and long-run production. The various metal stamping tools and technologies operate quickly, ensuring jobs are completed with faster turnaround times than any other method in the industry.
Long-Term Cost Efficiency
Metal stamping tools are affordable up front, and their maintenance costs are fairly low as well. When you combine those aspects with durable tools, accurate results, and automation capabilities that reduce labor costs, you get a level of cost efficiency that can’t be matched.
Questions? Contact Moeller Precision Tool
For high-quality metal stamping, you need high-quality die components. At Moeller Precision Tool, that’s what we do best. As a trusted global supplier of standard and special die components, we’re committed to delivering excellence to each and every one of our customers.
Have questions? We’re here to answer them. Whether you’re interested in learning more about our products and services or you’re on the lookout for a new career opportunity, don’t hesitate to contact our team online.